Battery charger for general purpose usage.
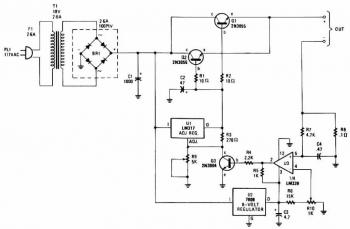
The charger's output voltage is adjustable and regulated, and has an adjustable constant-current charging circuit that makes it easy to use with most NiCad batteries. The charger can charge a single cell or a number of series-connected cells up to a maximum of 18V.
Power transistors Q1 and Q2 are connected as series regulators to control the battery charger's output voltage and charge-current rate. An LM-317 adjustable voltage regulator supplies the drive signal to the bases of power transistor Q1 and Q2. Potensiometer R9 sets the output-voltage level. A current sampling resistor, R8 (a 0.1 ohm/5W unit), is connected between the negative output lead and circuit ground. For each amp of charging current that flows through R8, a 100mV output is developed across it. The voltage developed across R8 is fed to one input of comparator U3. The other input of the comparator is connected to variable resistor R10.
As the charging voltage across the battery begins to drop, the current through R8 decrease. Then the voltage feeding pin 5 of U3 decreases, and the comparator output follows, turning Q3 back off, which completes the signal's circular path to regulate the battery's charging current.
The charging current can be set by adjusting R10 for the desired current. The circuit's output voltage is set by R9
The charger's output voltage is adjustable and regulated, and has an adjustable constant-current charging circuit that makes it easy to use with most NiCad batteries. The charger can charge a single cell or a number of series-connected cells up to a maximum of 18V.
Power transistors Q1 and Q2 are connected as series regulators to control the battery charger's output voltage and charge-current rate. An LM-317 adjustable voltage regulator supplies the drive signal to the bases of power transistor Q1 and Q2. Potensiometer R9 sets the output-voltage level. A current sampling resistor, R8 (a 0.1 ohm/5W unit), is connected between the negative output lead and circuit ground. For each amp of charging current that flows through R8, a 100mV output is developed across it. The voltage developed across R8 is fed to one input of comparator U3. The other input of the comparator is connected to variable resistor R10.
As the charging voltage across the battery begins to drop, the current through R8 decrease. Then the voltage feeding pin 5 of U3 decreases, and the comparator output follows, turning Q3 back off, which completes the signal's circular path to regulate the battery's charging current.
The charging current can be set by adjusting R10 for the desired current. The circuit's output voltage is set by R9
Comments